Documentation Revision Date: 2025-12-08
Dataset Version: 1
Summary
This dataset holds 3,530 files in netCDF format.
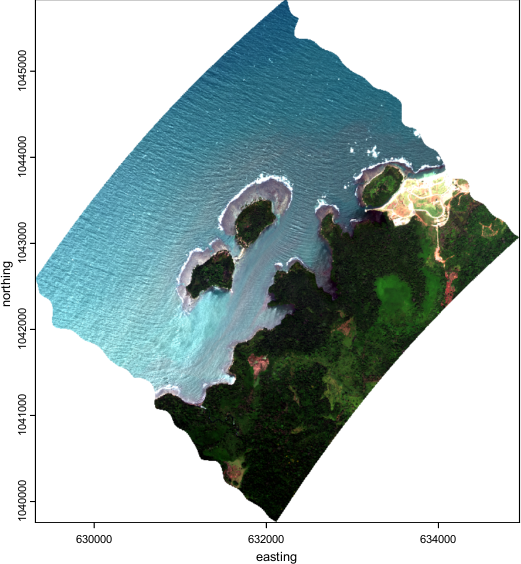
Figure 1. RGB color image derived from AVIRIS-3 orthocorrected surface reflectance data (R 686.18 nm, G 537.04 nm, B 470.05 nm) acquired on 2025-02-06 over the Protobelo District of the Colon Province, Panama (approximately 9.429 latitude, -79.795 longitude). Source: AV320250206t174741_000_L2A_OE_5988d8f5_RFL_ORT.nc
Citation
Brodrick, P.G., A.M. Chlus, R. Eckert, J.W. Chapman, M. Eastwood, S. Geier, S.R. Lundeen, W. Olson-Duvall, L.M. Rios, D.J. Jensen, M. Bernas, D.R. Thompson, and R.O. Green. 2025. AVUELO AVIRIS-3 Orthocorrected Surface Reflectance (provisional calibration). ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2479
Table of Contents
- Dataset Overview
- Data Characteristics
- Application and Derivation
- Quality Assessment
- Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
- Data Access
- References
Dataset Overview
This dataset contains Level 2A (L2A) orthocorrected surface reflectance and uncertainty estimates from the Airborne Visible / Infrared Imaging Spectrometer-3 (AVIRIS-3) instrument acquired for the Airborne Validation Unified Experiment: Land to Ocean (AVUELO) project in 2025. This L2A data product was generated with a provisional calibration algorithm. AVUELO aims to advance the validation and calibration of spaceborne imaging spectroscopy (hyperspectral) data for tropical ecosystems by combining airborne imaging spectroscopy for terrestrial and marine sites in Panama and Costa Rica with contemporaneous field measurements and data collected in February 2025. When available, a version 2 calibration Level 2A (L2A) of orthocorrected surface reflectance and uncertainty data for these same flight lines will be available in an AVIRIS-3 L2A Orthocorrected Surface Reflectance, Facility Instrument Collection, Version 2.
The NASA AVIRIS-3 is a spectral mapping system that measures reflected radiance at ~7.4-nm intervals in the Visible to Shortwave Infrared (VSWIR) spectral range from 390-2500 nm. The AVIRIS-3 sensor has a 40 degree instantaneous field of view with 1234 pixels, providing altitude dependent ground sampling distances from 12 m to sub meter range. This spectrometer measures radiance from surface and atmosphere and is identical in design to the orbital Earth Surface Mineral Dust Source Investigation (EMIT) spectrometer. AVIRIS-3 was deployed on a King Air aircraft.
Surface hemispherical directional reflectance was derived from calibrated radiance using an optimal estimation algorithm. For each flight scene, two file types are included: orthocorrected surface reflectance (RFL_ORT) and orthocorrected reflectance uncertainty (UNC_ORT) in netCDF format. Both file types include data projected in a UTM coordinate system.
Project: AVUELO
Airborne Validation Unified Experiment Land to Ocean (AVUELO) is a NASA investigation that aims to advance the validation of spaceborne hyperspectral data for tropical ecosystems by combining airborne hyperspectral imagery for terrestrial and marine sites in Panama and Costa Rica with contemporaneous field measurements and collections in February 2025. This campaign was led and supported by NASA and the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama, with additional major contributions from other scientists and institutions. NASA’s Airborne Visible-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer 3 (AVIRIS-3) was deployed to collect hyperspectral imagery. Terrestrial collection in Panama encompassed many intensively studied sites and wide variation in soil type, geology, rainfall, and vegetation type. In Costa Rica, AVUELO focused on Rincon de la Vieja and Turrialba volcanoes, well-studied forests sites, and Pacific coastal areas in collaboration with the Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) team. Associated terrestrial field work focused on acquiring data on the traits and taxonomic identity of canopy plant species captured in the airborne imagery.
Related Publication
Green, R.O., M.E. Schaepman, P. Mouroulis, S. Geier, L. Shaw, A. Hueini, M. Bernas, I. McKinley, C. Smith, R. Wehbe, M. Eastwood, Q. Vinckier, E. Liggett, S. Zandbergen, D. Thompson, P. Sullivan, C. Sarture, B. Van Gorp, and M. Helmlinger. 2022. Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer 3 (AVIRIS-3). 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO). https://doi.org/10.1109/AERO53065.2022.9843565
Related Datasets
Eckert, R., D.R. Thompson, A.M. Chlus, J.W. Chapman, M. Eastwood, M. Bernas, S. Geier, M. Helmlinger, D. Keymeulen, E. Liggett, S. Nadgauda, L.M. Rios, L.A. Shaw, W. Olson-Duvall, P.G. Brodrick, and R.O. Green. 2024. AVIRIS-3 L1B Calibrated Radiance, Facility Instrument Collection. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2356
Brodrick, P.G., A.M. Chlus, U.N. Bohn, E. Greenberg, J. Montgomery, J.W. Chapman, M. Eastwood, S.R. Lundeen, R. Eckert, W. Olson-Duvall, D.R. Thompson, and R.O. Green. 2025. AVIRIS-3 L2A Orthocorrected Surface Reflectance, Facility Instrument Collection. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2357
- Facility Instrument collection for the AVIRIS-3 instrument with L1B radiance and L2A reflectance products
Acknowledgement
AVUELO is a partnership between NASA, the Smithsonian Institution’s Tropical Research Institute, and the Costa Rican Fisheries Federation, as well as universities and institutes in the United States and Panama.
Data Characteristics
Spatial Coverage: Panama, Costa Rica, and nearby Pacific Ocean
Spatial Resolution: 1.1 to 4.4 m (altitude dependent)
Temporal Bounds: 2025-02-06 to 2025-02-28
Temporal Resolution: One-time estimate
Study Area: (All latitudes and longitudes given in decimal degrees)
| Site | Northernmost Latitude | Southernmost Latitude | Westernmost Longitude | Easternmost Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Costa Rica, Panama, and Pacific Ocean | 10.9102 | 7.1483 | -85.7051 | -79.32133 |
Data File Information
This dataset includes surface reflectance and surface reflectance uncertainty in netCDF format. There are 3,530 files with two files per flight scene.
The file naming convention is <flight prefix>_<id>_L2A_OE_<ver>_<product>.nc, where
- <flight prefix> = flight line identifier, AV3YYYMMDDthhmmss, encoding the date and time by year (YYYY), month (MM), day (DD), hour (hh), minute (mm), and second (ss) of the flight (e.g., AV320230711t225833).
- <id> = scene-id from within a flight line.
- <ver> = unique seven character identifier of full heritage versioning.
- <product> = L2A data product: “RFL_ORT'' for orthocorrected surface reflectance or “UNC_ORT'' for reflectance uncertainty.
Example file names for one flight scene are:
- AV320250206t174741_000_L2A_OE_5988d8f5_RFL_ORT.nc
- AV320250206t174741_000_L2A_OE_5988d8f5_UNC_ORT.nc
The surface reflectance (RFL) and reflectance uncertainty (UNC_ORT) files hold orthocorrected data projected into the UTM coordinate system using WGS-84 datum. Projection information is included with attributes of the transverse_mercator variable in these files. Nodata values are set to -9999.
These data are distributed as multifile granules in Earthdata Search. Each granule includes the surface reflectance and the uncertainty netCDFs. The granule naming convention is <flight prefix>_<id>_L2A_OE_<ver>_RFL_ORT.
Table 1. Variables in surface reflectance (RFL_ORT) and reflectance uncertainty (UNC_ORT) files.
| Variable | Description | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Both RFL_ORT and UNC_ORT | ||
| easting | UTM easting coordinate for center of grid cell for orthocorrected pixel location | m |
| northing | UTM northing coordinate for center of grid cell for orthocorrected pixel location | m |
| transverse_mercator | Spatial reference information for the UTM coordinate reference system used | - |
| wavelength | Center wavelength for each spectral band (n = 284) | nm |
| fwhm | Full width at half maximum for band (n = 284) | nm |
| RFL_ORT only | ||
| reflectance | Surface hemispherical directional reflectance factor in 284 bands covering wavelengths between 390 nm to 2500 nm in approximately 7.4-nm intervals, estimated using an optimal estimation based atmospheric correction algorithm | 1 |
| aerosol_optical_thickness | Factor measuring absorption or optical pathlength of measured radiance; level of aerosols in atmosphere | 1 |
| water_vapor | Level of water vapor in the atmosphere between sensor and surface measured in linear units of condensed liquid. | cm |
| UNC_ORT only | ||
| uncertainty | Uncertainty in surface hemispherical directional reflectance given in standard deviation units and estimated using an optimal estimation based atmospheric correction algorithm | 1 |
Application and Derivation
AVUELO is a NASA project that aims to advance the validation and calibration of spaceborne imaging spectroscopy (hyperspectral) data for tropical ecosystems by combining airborne imaging spectroscopy for terrestrial and marine sites in Panama and Costa Rica with contemporaneous field measurements and data collected in February 2025.
Associated terrestrial field work focused on acquiring data on the traits and taxonomic identity of canopy plant species captured in the airborne imagery. An intensive program of canopy leaf collections took place close in time to the overflights. On-going field work includes mapping crowns over >150 ha of mapped forest plots with high spatial precision, to enable linkage of pixels in the airborne data to species identity of canopy trees and lianas.
AVIRIS-3 also collected data over coastal waters off the Pacific to support calibration and validation of PACE, a hyperspectral satellite sensor focused partly on oceanic observations.
Quality Assessment
The AVIRIS-3 calibration procedure addresses electronic effects involving radiometric responses of each detector, optical effects involving the spatial and spectral view of each detector, and radiometric calibration. Detector responsiveness is measured at the beginning of each deployment and mid-flight for particularly long deployments. Instrument artifacts in the spectrometer data, such as striping, are removed statistically by minimizing a Markov Random Field model. Likewise, bad pixels are identified and corrected using statistical methods followed by laboratory and field protocols to evaluate effectiveness. Details of calibration methods are available in Chapman et al. (2019).
Data Acquisition, Materials, and Methods
AVUELO aims to advance the validation and calibration of spaceborne imaging spectroscopy (hyperspectral) data for tropical ecosystems by combining airborne imaging spectroscopy for terrestrial and marine sites in Panama and Costa Rica with contemporaneous field measurements and data collected in February 2025.
NASA’s Airborne Visible-Infrared Imaging Spectrometer 3 (AVIRIS-3) was deployed on a King Air aircraft to collect hyperspectral imagery between February 6 and February 28, 2025 (Figure 2). Terrestrial collections in Panama encompassed many intensively studied sites having a wide variation in soil type, geology, rainfall, and vegetation type. These included managed landscapes, secondary forests of varying ages, and old-growth forests in lowland, montane, and coastal habitats (e.g. mangroves). All areas were collected at 3-m spatial resolution, with intensively studied focal areas of particular interest collected at 1-m resolution. In Costa Rica, AVUELO focused on Rincon de la Vieja volcano to assess differences in vegetation growth due to natural CO2 enhancements. AVIRIS-3 also collected data over coastal waters off the Pacific to support calibration and validation of PACE, a hyperspectral satellite sensor focused partly on oceanic observations.
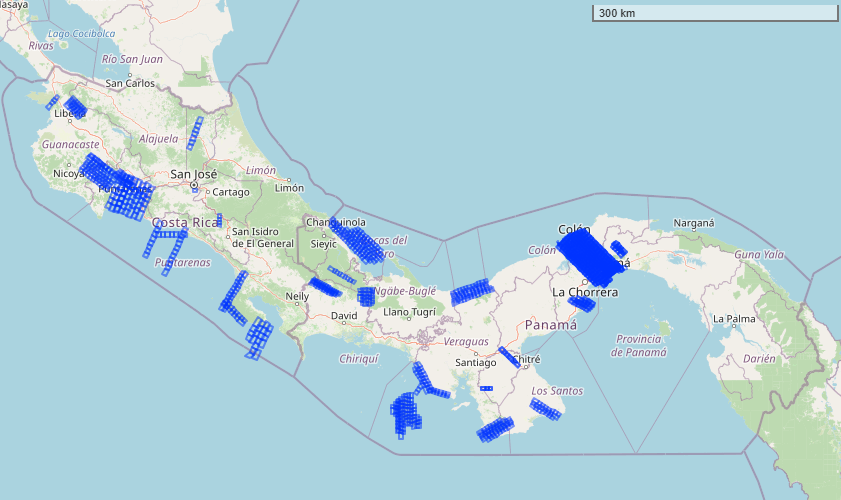
Figure 2. Locations of flight scenes over Costa Rica, Panama, and eastern Pacific Ocean represented as blue rectangular polygons. Basemap: © OpenStreetMap contributors.
AVIRIS-3 measures surface and atmospheric radiances in the wavelength range from 390 nm to 250 nm with 7.4-nm sampling. Spectra are measured as images with 1,234 cross-track elements and spatial sampling from 0.3 m to 10.0 m, depending on sensor-to-surface distance. It is a cryogenic instrument with advanced system control and real-time onboard spectroscopic data processing algorithms evolved from AVIRIS-NG. The radiometric range is from 0 to max terrestrial Lambertian radiance with higher signal-to-noise ratio performance than AVIRIS-Classic or AVIRIS-Next Generation. The spatial field-of-view is 39.5 degrees with 0.56 milliradian sampling (Green et al., 2022).
This Level 2A collection contains surface reflectance data for 284 bands in orthocorrected format. L2A reflectances were derived from the associated L1B radiance data. The surface reflectance product (RFL_ORT) includes the hemispherical-directional reflectance factor for every pixel in the scene. Reflectance is estimated from at-sensor radiance (Level 1B) using an optimal estimation (OE) based atmospheric correction procedure, fully described in the EMIT Level 2A ATBD (Thompson et al., 2020).
The OE algorithm produces two estimates for each pixel: surface reflectance and reflectance uncertainty. The reflectance uncertainty map (UNC_ORT) was derived from the diagonal elements of the posterior covariance matrix, square-rooted, to provide a spectrum of uncertainty about the reflectance estimate in standard deviations units. Together, these two products define the posterior probability of the surface reflectance given the at-sensor radiance measurement, captured as a multivariate normal distribution. Uncertainty-aware downstream analysis of reflectance can leverage both products, using the reflectance uncertainty as error bars over the reflectance estimate.
Pixel locations are provided in projected UTM coordinates. Nodata values are set to -9999.
Data Access
These data are available through the Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) Distributed Active Archive Center (DAAC).
AVUELO AVIRIS-3 Orthocorrected Surface Reflectance (provisional calibration)
Contact for Data Center Access Information:
- E-mail: uso@daac.ornl.gov
- Telephone: +1 (865) 241-3952
References
Chapman, J.W., D.R. Thompson, M.C. Helmlinger, B.D. Bue, R.O. Green, M.L. Eastwood, S. Geier, W. Olson-Duvall, and S.R. Lundeen. 2019. Spectral and radiometric calibration of the Next Generation Airborne Visible Infrared Spectrometer (AVIRIS-NG). Remote Sensing 11:2129. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs11182129
Eckert, R., D.R. Thompson, A.M. Chlus, J.W. Chapman, M. Eastwood, M. Bernas, S. Geier, M. Helmlinger, D. Keymeulen, E. Liggett, S. Nadgauda, L.M. Rios, L.A. Shaw, W. Olson-Duvall, P.G. Brodrick, and R.O. Green. 2024. AVIRIS-3 L1B Calibrated Radiance, Facility Instrument Collection. ORNL DAAC, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. https://doi.org/10.3334/ORNLDAAC/2356
Green, R.O., M.E. Schaepman, P. Mouroulis, S. Geier, L. Shaw, A. Hueini, M. Bernas, I. McKinley, C. Smith, R. Wehbe, M. Eastwood, Q. Vinckier, E. Liggett, S. Zandbergen, D. Thompson, P. Sullivan, C. Sarture, B. Van Gorp, and M. Helmlinger. 2022. Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer 3 (AVIRIS-3). 2022 IEEE Aerospace Conference (AERO). https://doi.org/10.1109/AERO53065.2022.9843565
Green, R.O., M.L. Eastwood, C.M. Sarture, T. G. Chrien, M. Aronsson, B.J. Chippendale, J.A. Faust, B.E. Pavri, C. J. Chovit, M. Solis, M.R. Olah, and O. Williams. 1998. Imaging spectroscopy and the Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS). Remote Sensing of Environment 65:227- 248. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0034-4257(98)00064-9
Thompson, D.R, P.G. Brodrick, R.O. Green, O. Kalashnikova, S. Lundeen, G. Okin, W. Olson-Duvall, and T. Painter. 2020. EMIT L2A Algorithm: Surface Reflectance and Scene Content Masks: Theoretical Basis. Version 1.0. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology; Pasadena, California. https://earth.jpl.nasa.gov/emit/internal_resources/281